Project Control Process
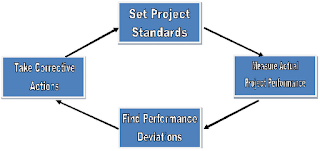 |
| Project Control Process |
- Setting Project Standards: Targets are set for each project activity in terms of time, cost, quality etc. They serve ads standards for control. Project planning is used to set such standards.
- Performance Monitoring: Actual performance of each project activity is measured to provide feedback. Project reporting system is the source of such information.
- Find Performance Deviations: The actual performance is compared with the standards to find out deviation for each activity. The causes and incidence of deviatiions are analyzed.
- Corrective Actions: Corrective actions are taken to improve performance in future period. This is the crux of project control. It remedies the deviations to keep the system stable.
- Project control system should focus on critical points in which performance deviatiions cause the greatest damage to the project. It should find and resolve problems to get the project back on track.
Areas for Project Control
- Time Control: Time control can be of two types:
- Normal Time Control: It is the estimated time for completion of an activity. Increase beyond this time is not likely to result in cost reduction.
- Crash Time Control: It is the estimated time of completion of an activity which cannot be reduced further irrespective of cost considerations.
- Every project has an optimal time schedule which is effectively controlled to check overruns. Time delays result in cost overruns.
- Cost Control: It involves the following:
- Setting up standard costing and budgetary control systems for the project. Project accounts capture costs as they are committed.
- Allocating responsibilities for cost control at task level.
- Ensuring proper allocation of costs to project codes; ensuring that costs are properly authorized.
- Measuring actual costs and comparing them with standard costs to prepare cost reports.
- Identifying deviations to take corrective actions to control cost overruns and maintain financial discipline.
- Value engineering can be used for Cost Reduction.
Types of Project Costs can be:
- Budgeted Cost: Estimated during project planning.
- Contracted Cost: Cost provided in the contract.
- Committed Cost: Cost of purchase orders issued.
- Earned Value: Cost of work in progress.
- Invoiced Cost: Accrued Cost/ Invoice by contractor.
- Incurred Cost: Payment authorized.


No comments:
Post a Comment